Progressive Delivery Using Flagger Enterprise
Built upon the core tenets of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), progressive delivery involves gradually rolling out features to small groups of select users to balance performance with speed. Developers and DevOps teams use fine-grained controls to minimize the risks of pushing new features to the production environment. If the newly released feature proves to be stable and performant, it can then be released to all users.
Flagger is a progressive delivery operator for Kubernetes and part of the Flux family of open source projects. It reduces the risk of introducing new software versions and automates production releases to improve your time to delivery. Flagger implements deployment strategies—canary releases, A/B testing, Blue/Green mirroring—using a service mesh (App Mesh, Istio, Linkerd, Kuma, Open Service Mesh) or an ingress controller (Contour, Gloo, NGINX, Skipper, Traefik, APISIX) for traffic routing. For release analysis, Flagger can query Prometheus, InfluxDB, Datadog, New Relic, CloudWatch, Stackdriver, or Graphite. For alerting it uses Slack, MS Teams, Discord, and Rocket. Using Flux allows us to manage our cluster applications in a declarative way through changes in a Git repository.
Weave GitOps Enterprise integrates with Flagger in order to provide a view on progressive delivery deployments. This includes the ability to view all the resources that Flagger manages during its operation. The default ClusterRole gitops-canaries-reader includes the minimum permissions necessary for a user to be able to view canary object details, metric template object details and canary related events.
The WGE UI's Applications > Delivery view provides an "at a glance" view so that you can understand the status of your progressive delivery rollouts across a fleet of connected clusters. This removes the cognitive overhead of having to know which objects to query and where they are located. You can also drill down into each rollout to understand its status and configuration, and view near-to-realtime data on any summary or details page.
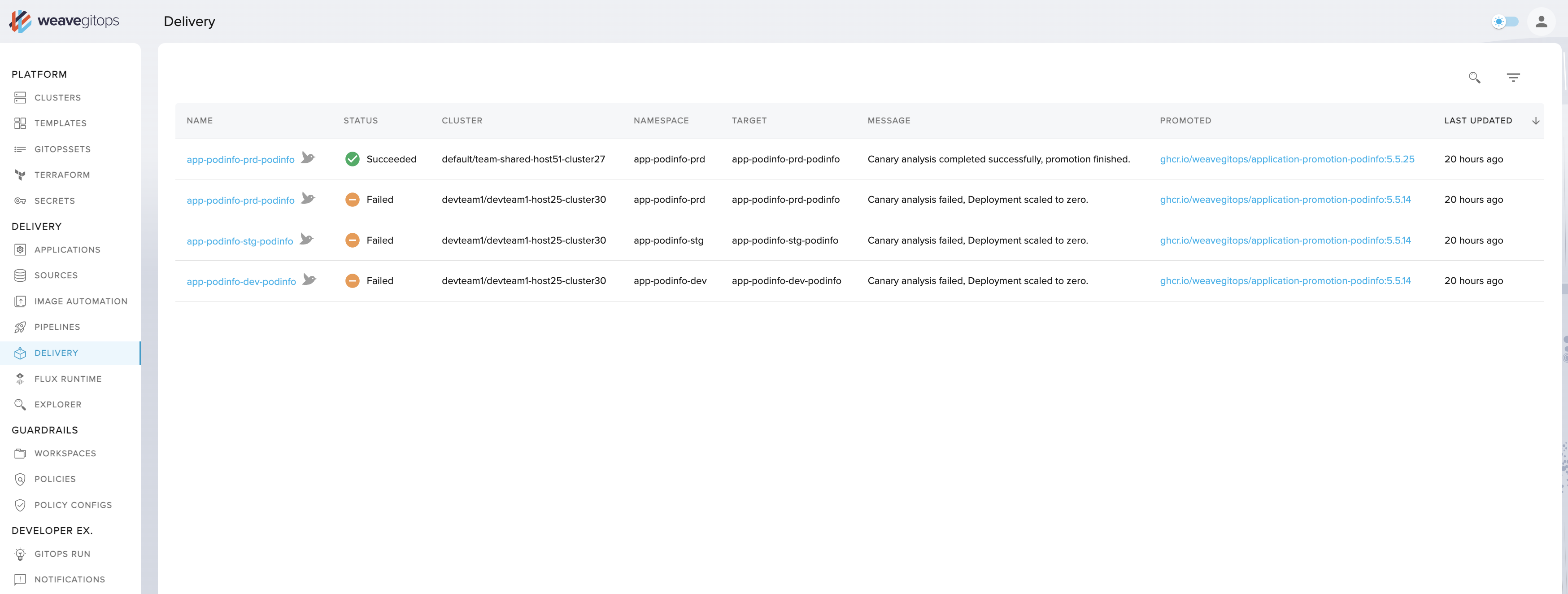
How to use WGE's progressive delivery offering:
- if you don’t have Flagger installed on any clusters, you'll receive an onboarding message about installing it
- click on the delivery tab on the menu bar to retrieve a table view of canaries with key summary information regarding their location and state
- click on a canary to see more detailed information about status, gates, and other elements
- click on the events tab on the detail page to see the most recent Kubernetes events for that canary and learn more about deployment history
- click on the yaml tab on the detail page to see the raw yaml of the canary
- view objects from any cluster/namespace that you have the appropriate permissions for, and nothing else
Supported deployment strategies include:
Canary Release: the system gradually shifts traffic to
a new version of an application and assesses performance—either promoting the release or abandoning it, based on performance.
A/B Testing: uses HTTP headers or cookies to ensure users remain on the same version of an application during a canary analysis.
Blue/Green: Traffic is switched from the current application to a new version based on the success of testing.
Blue/Green with Traffic Mirroring: sends copies of incoming requests to the new version of an application. The user receives the response from the current application and the other is discarded. The new version is promoted only if metrics are healthy.
This guide uses Flux manifests to install Flagger and Linkerd, a CNCF project and service mesh for Kubernetes and beyond. We will walk you through a full end-to-end scenario where you will:
- Install the Linkerd service mesh
- Install Flagger
- Deploy a sample application using a canary release strategy based on metrics provided through Linkerd's in-built Prometheus instance
Prerequisites
- This guide assumes you already have a Kubernetes cluster running and have bootstrapped Flux. To apply the manifests listed here, you will need to commit them to a repository being reconciled with Flux.
- Flagger requires the
autoscaling/v2orautoscaling/v2beta2API to be installed on your cluster. You can usekubectl api-resourcesto check which API versions are supported. - The step CLI installed to generate certificates that support mTLS connections.
Installing Linkerd Using Flux
To install Linkerd we'll use a Kustomization file. It will allow us to specify the order and default namespace for the installed resources, and to generate Secrets from certificate files via the use of a secretGenerator.
To support mTLS connections between meshed pods, Linkerd requires a trust anchor
certificate and an issuer certificate with its corresponding key. These certificates are
automatically created via the linkerd install command. However, when using a Helm chart to
install Linkerd, you must provide these certificates deliberately. The step CLI, listed above, allows us to generate these
certificates.
To generate the trust anchor certificate, run:
step certificate create root.linkerd.cluster.local ca.crt ca.key \
--profile root-ca --no-password --insecure
To generate the issuer certificate, run:
step certificate create identity.linkerd.cluster.local issuer.crt issuer.key \
--profile intermediate-ca --not-after 8760h --no-password --insecure \
--ca ca.crt --ca-key ca.key
Add the ca.crt, issuer.crt, and issuer.key files to the cluster repository under a linkerd
directory.
Let's add the three manifests for Linkerd components under the ./linkerd directory:
- A
Namespaceresource to control where the components are installed - A
HelmRepositoryresource to make the Linkerd Helm repo available on the cluster - A
HelmReleaseresource to install the latest version of Linkerd from theHelmRepository
Expand to see and copy-paste the three Linkerd manifests to add
Next, add the following manifests. The first file instructs Kustomize to patch any Secrets that are referenced in
HelmRelease manifests. The second file is a Kustomization that references all the
other linkerd resource files.
Expand to see the Linkerd Kustomization manifests
At this point the linkerd directory in your cluster repository should look like this:
> tree linkerd
linkerd
├── ca.crt
├── issuer.crt
├── issuer.key
├── kustomization.yaml
├── kustomizeconfig.yaml
├── namespace.yaml
├── releases.yaml
└── source.yaml
Once Flux reconciles this directory to the cluster, Linkerd should be installed.
Before proceeding to the next step, check that all the Linkerd pods have started successfully:
> kubectl get pods -n linkerd
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
linkerd-destination-66d5668b-4mw49 4/4 Running 0 10m
linkerd-identity-6b4658c74b-6nc97 2/2 Running 0 10m
linkerd-proxy-injector-6b76789cb4-8vqj4 2/2 Running 0 10m
> kubectl get pods -n linkerd-viz
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-db56d7cb4-xlnn4 2/2 Running 0 10m
metrics-api-595c7b564-724ps 2/2 Running 0 10m
prometheus-5d4dffff55-8fscd 2/2 Running 0 10m
tap-6dcb89d487-5ns8n 2/2 Running 0 10m
tap-injector-54895654bb-9xn7k 2/2 Running 0 10m
web-6b6f65dbc7-wltdg 2/2 Running 0 10m
Any new directories that you add to the cluster repository while following this guide must be included in a path that Flux reconciles.
Installing Flagger Using Flux
To install Flagger, you'll use a Kustomization file that will define the installation order and provide a default namespace for the installed resources.
Create a new flagger directory. Make sure to locate it under a repository path that Flux reconciles.
Now add under this directory the three resource manifests for Flagger:
- A
Namespaceresource to control where the components are installed - A
HelmRepositoryresource to make the Flagger Helm repo available on the cluster - A
HelmReleaseresource to install the latest version of Flagger and the load tester app (which generates synthetic traffic during the analysis phase), from thatHelmRepository
Expand to see the three Flagger resource manifests
Now add the following Kustomization file. It references all of the previous files that you've added:
Expand to see the Flagger Kustomization manifest
The flagger directory in the cluster repository should look like this:
> tree flagger
flagger
├── kustomization.yaml
├── namespace.yaml
├── releases.yaml
└── source.yaml
Once Flux reconciles this directory to the cluster, Flagger and the load tester app should be installed.
Before proceeding to the next step, check that all of your Flagger pods have started successfully:
> kubectl get pods -n flagger
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
flagger-7d456d4fc7-knf2g 1/1 Running 0 4m
loadtester-855b4d77f6-scl6r 1/1 Running 0 4m
Custom Resources Generated by Flagger
When Flagger is configured to integrate with a service mesh such as Linkerd or Istio for the rollout, this ClusterRole needs to be extended so that it can read the additional service mesh resources that Flagger generates. To display service mesh- or ingress-related resources, we require spec.provider to be set in each canary resource.
The following table provides a list of all the custom resources that Flagger generates grouped by provider:
| Provider | API Group | Resource |
|---|---|---|
| AppMesh | appmesh.k8s.aws | virtualnode |
| appmesh.k8s.aws | virtualrouter | |
| appmesh.k8s.aws | virtualservice | |
| Linkerd | split.smi-spec.io | trafficsplit |
| Istio | networking.istio.io | destinationrule |
| networking.istio.io | virtualservice | |
| Contour | projectcontour.io | httpproxy |
| Gloo | gateway.solo.io | routetable |
| gloo.solo.io | upstream | |
| Nginx | networking.k8s.io | ingress |
| Skipper | networking.k8s.io | ingress |
| Traefik | traefik.containo.us | traefikservice |
| Open Service Mesh | split.smi-spec.io | trafficsplit |
| Kuma | kuma.io | trafficroute |
| GatewayAPI | gateway.networking.k8s.io | httproute |
For example, the following manifest shows how gitops-canaries-reader has been extended to allow the user for viewing TrafficSplit resources when Linkerd is used:
Expand to see example canary reader RBAC
Setting up Remote Cluster Permissions
In order to view canaries in a remote cluster from the management cluster, you need to consider the following:
- The service account used to access the remote cluster needs to be able to list namespaces and custom resource definitions in the given cluster. It additionally needs to be able to impersonate users and groups.
- The user or group that logs in to the management cluster, needs appropriate permissions to certain resources of the remote cluster.
For example, applying the following manifest on remote clusters, ensures that the wego-admin user will be able to view canary information from within the Weave GitOps Enterprise UI on the management cluster:
Expand to see example of remote cluster canary reader
You may need to add more users/groups to the read-canaries ClusterRoleBinding to ensure additional users can view canary information from within the Weave GitOps Enterprise UI.
Deploy a Canary Release
To demonstrate the progressive rollout of an application, we'll use a tiny sample web app called podinfo and configure a canary release strategy.
In our example, Flagger will scale up a new version of podinfo (the canary) alongside the existing version (the primary). It will gradually increase traffic to the new version in increments of 5%, up to a maximum of 50%. Flagger will continuously monitor the new version for an acceptable request response rate and average request duration. Based on this analysis, Flagger will either update the primary to the new version or abandon the promotion, then scale the canary back down to zero.
Create a new test directory and add these three canary resource manifests under it:
- A
Namespaceresource to control where the components are installed - A
DeploymentandHorizontalPodAutoscalerfor thepodinfoapplication - A
Canaryresource which references theDeploymentandHorizontalPodAutoscalerresources
We don't need to define a service resource. This is specified within the canary definition and created by Flagger.
Expand to see the three canary resource manifests
Add a Kustomization file to apply all resources to the test namespace:
Expand to see the Canary Kustomization manifest
At this point, the test directory in the cluster repository should look like this:
> tree test
test
├── canary.yaml
├── deployment.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
└── namespace.yaml
After a short time, the status of the canary object should be set to Initialized:
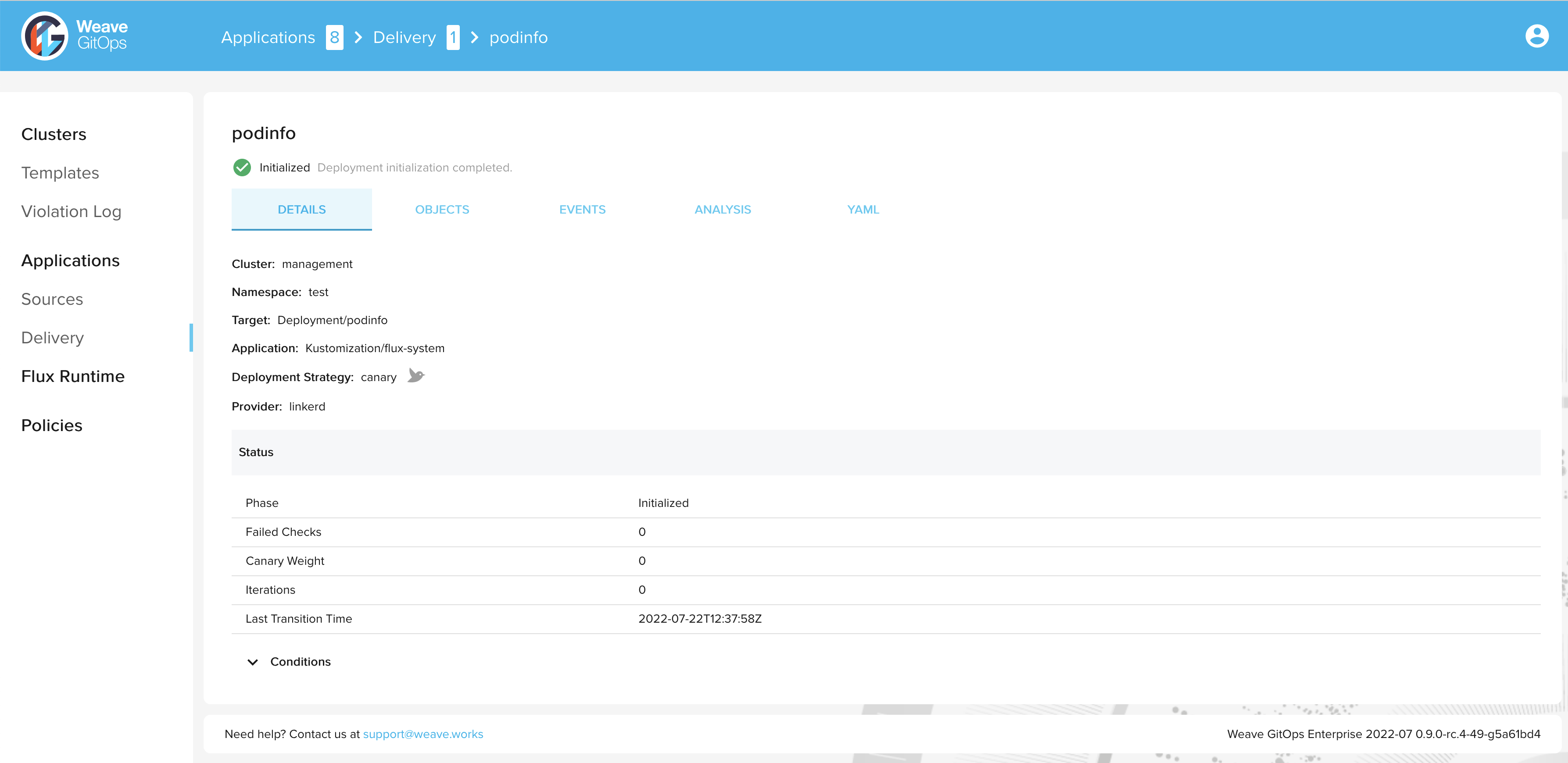
> kubectl get canary podinfo -n test
NAME STATUS WEIGHT LASTTRANSITIONTIME
podinfo Initialized 0 2022-07-22T12:37:58Z
Trigger a new rollout by bumping the version of podinfo:
> kubectl set image deployment/podinfo podinfod=ghcr.io/stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.1 -n test
During the progressive rollout, the canary object reports on its current status:
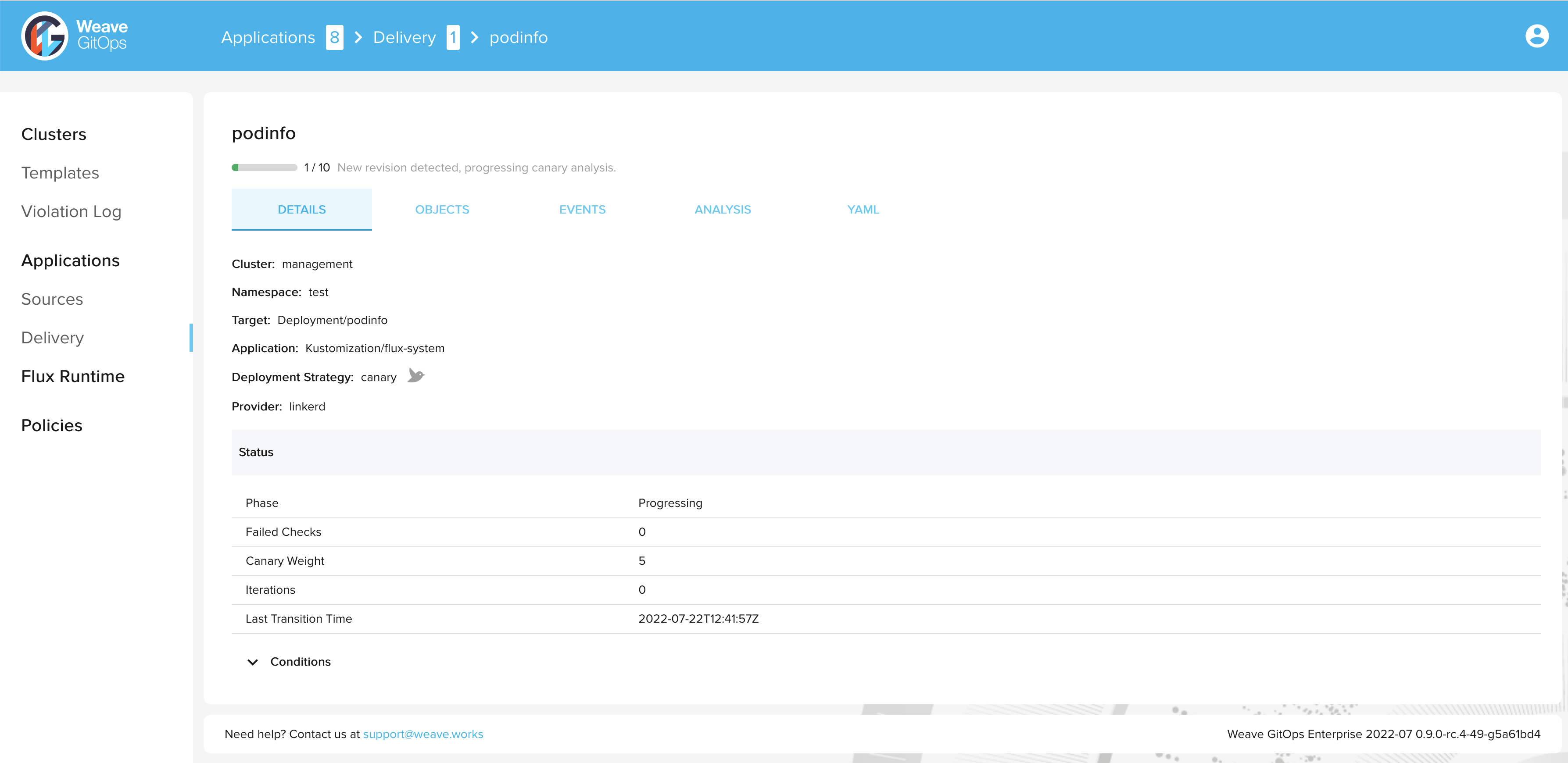
> kubectl get canary podinfo -n test
NAME STATUS WEIGHT LASTTRANSITIONTIME
podinfo Progressing 5 2022-07-22T12:41:57Z
After a short time the rollout is completed and the status of the canary object is set to
Succeeded:
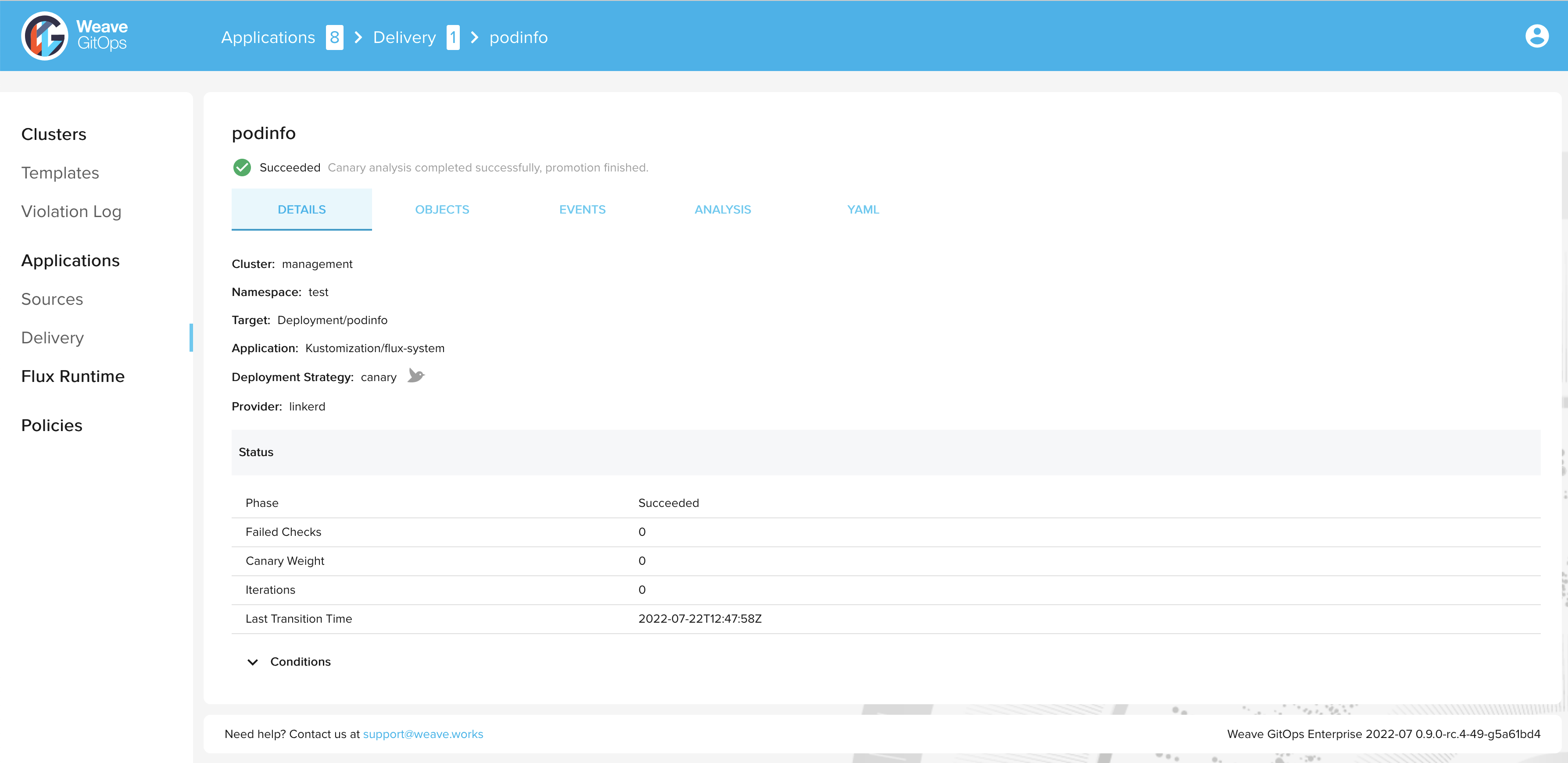
> kubectl get canary podinfo -n test
NAME STATUS WEIGHT LASTTRANSITIONTIME
podinfo Succeeded 0 2022-07-22T12:47:58Z
Summary
Congratulations, you have now completed a progressive delivery rollout with Flagger and Linkerd! 🎉
Next steps:
- Explore more of what Flagger offers
- Configure manual approvals for progressive delivery deployments