Getting started with secrets management Enterprise
This feature is in alpha and certain aspects will change
We're very excited for people to use this feature. However, please note that changes in the API, behaviour and security will evolve. The feature is suitable to use in controlled testing environments.
This guide shows you a basic experience to get started with Weave Gitops Secrets. It covers the scenario of setting up the capability in a test environment and how to use it for your applications.
Requirements
- You have a test Weave Gitops Enterprise environment with Flux installed.
- You have a secret in AWS secrets manager.
Add the secrets infra
In order to be able to manage external secrets stores and secrets, add external-secrets application from weaveworks-charts profiles repository.
Here you could refresh how to add applications.
Include via values.yaml the configuration to deploy the SecretStore
connecting to AWS Secrets Manager.
Expand to see an example
values:
secretStores:
enabled: true
path: ./clusters/bases/secrets
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
namespace: flux-system
This example points to the path clusters/bases/secrets in our configuration repo where a kustomization exists
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- aws-secrets-manager.yaml
With the AWS Secrets Manager secret store
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: SecretStore
metadata:
name: aws-secrets-manager
namespace: flux-system
spec:
provider:
aws:
auth:
secretRef:
accessKeyIDSecretRef:
key: access-key
name: awssm-secret
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
key: secret-access-key
name: awssm-secret
region: eu-north-1
service: SecretsManager
Review and merge the PR and see it available in your cluster
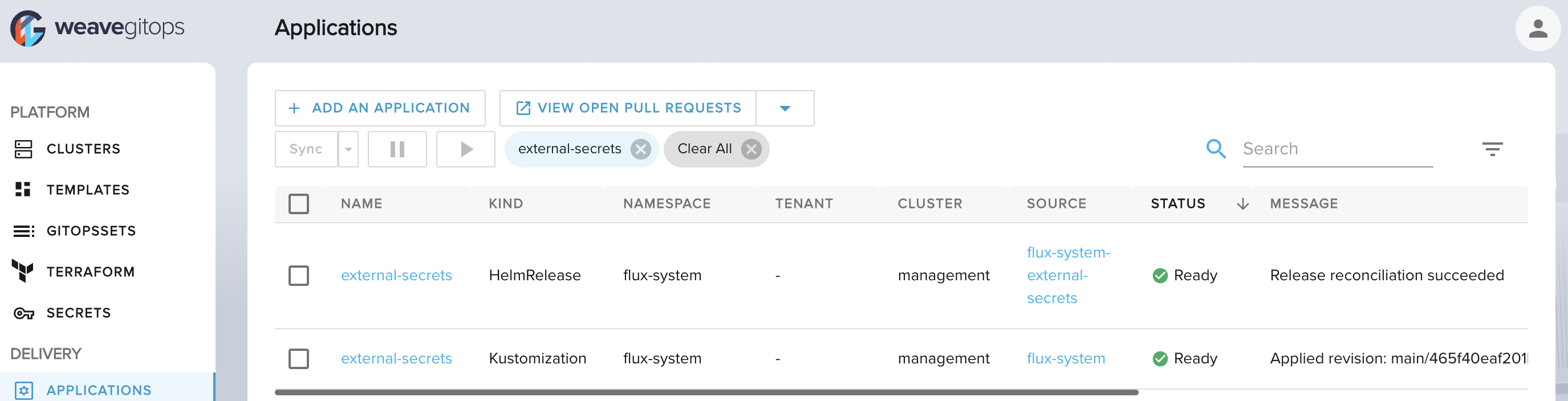
Create the secret
Given you have a secret in AWS Secrets Manager for example test/search/db.
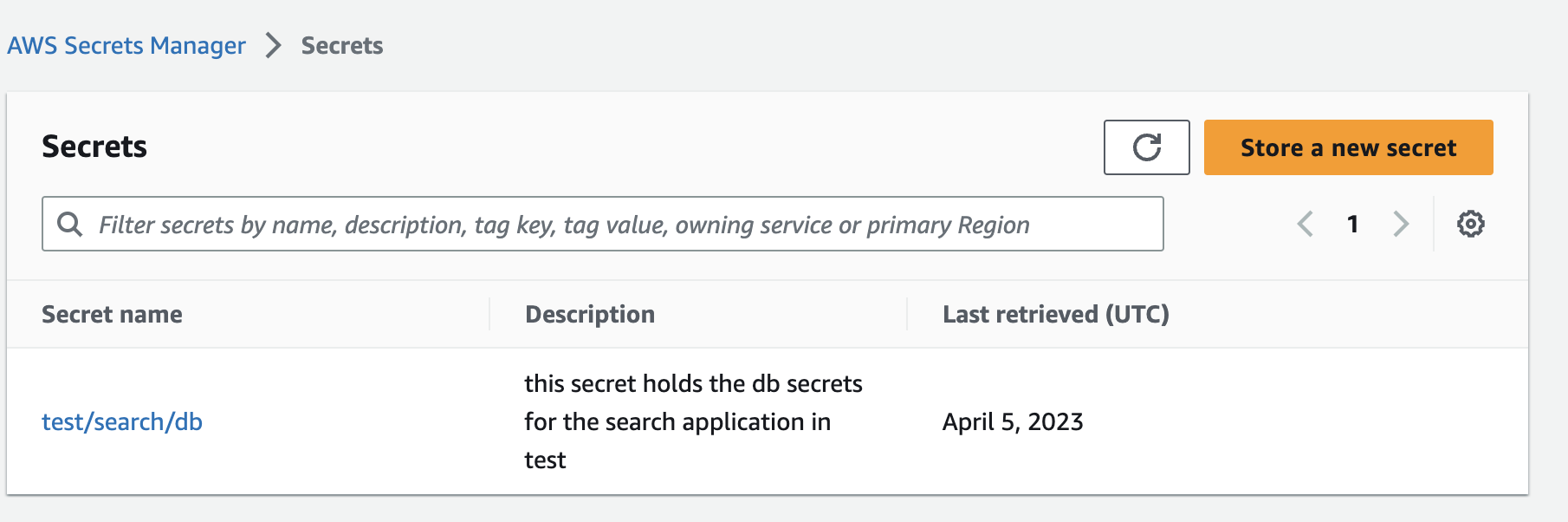
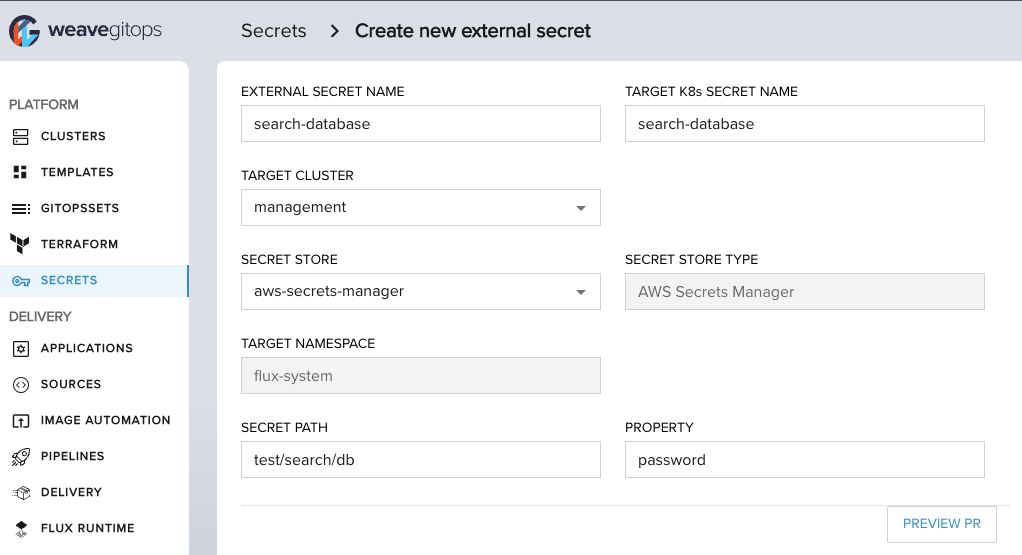
Create the External Secret manifest via Secrets UI to pull the secret from your store into your environment.
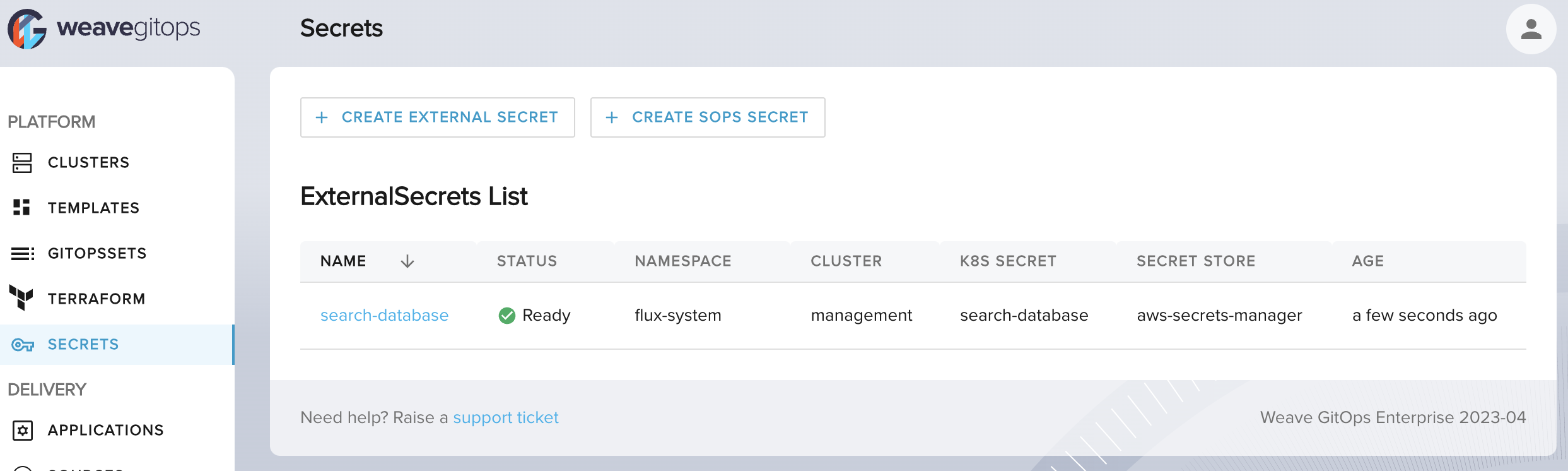
See it available in your cluster.
Use the secret
At this stage you have everything you need for your application to consume the secret. Add it to your application as usual.
Expand to see example
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: secret-dotfiles-pod
spec:
volumes:
- name: database-secrets
secret:
secretName: search-database
containers:
- name: dotfile-test-container
image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
command:
- ls
- "-l"
- "/etc/database-secrets"
volumeMounts:
- name: database-secrets
readOnly: true
mountPath: "/etc/database-secrets"
You could see the expected secret available
kubectl logs -f secret-dotfiles-pod
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Apr 5 17:26 password -> ..data/password
Next steps?
- For other setup scenarios using external secrets, see setup ESO
- For SOPS secrets, see setup SOPS
- To discover the UI capabilities to manage secrets, see here